Description
Many products are not yet listed. Please contact us for more product information.
If the product model differs from the displayed image, the model number shall prevail. Please contact us for specific product images; we will arrange to take photos in our warehouse for confirmation.
We have 76 shared warehouses worldwide, so it may sometimes take several hours to accurately return the information to you. We apologize for the inconvenience. Of course, we will respond to your inquiries as soon as possible.
Specific functions of this PCB card:
Control function: As the core component of the control unit, it is responsible for signal processing, power distribution, and equipment linkage (such as valve control and power system monitoring).
Energy management: Optimizes energy distribution in the ship’s power system, supports DC 12V power supply, and in some scenarios, involves energy visualization (such as the energy management system of NTT Facilities).
Signal integrity: Reduces parasitic parameters (capacitance, inductance, resistance) through precise PCB design, ensuring the stability of high-frequency/high-speed signal transmission and avoiding crosstalk, timing errors, or electromagnetic interference.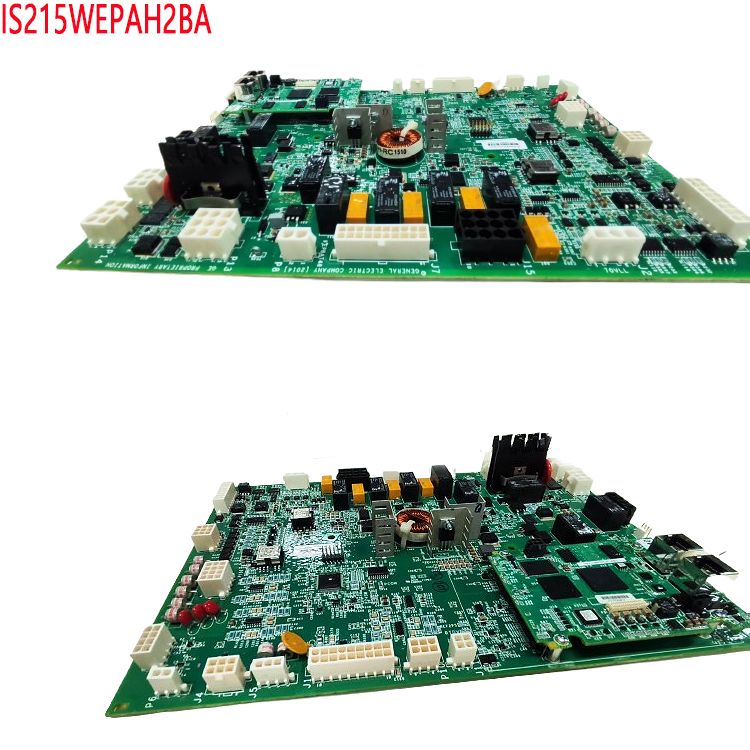
Installation and configuration: Requires matching with the corresponding control unit (such as the CEP-C type), and connects to sensors, actuators, and power modules through interfaces. PCB design specifications must be followed, such as controlling impedance, minimizing vias, and avoiding right-angle bends to ensure signal integrity.
Parameter Settings: Supports user card management (e.g., adding/deleting access permissions), adjusting start-up time settings, and a maximum reading distance of approximately 15cm (requires a dedicated card reader).
Power Supply Requirements: Typically uses DC 12V power supply. Ensure low inductance and low resistance in the power path to prevent voltage fluctuations from affecting device stability.
Performance Optimization: Improves signal integrity and reduces crosstalk and noise through multi-layer design, high-speed signal routing (e.g., 50Ω impedance control), and decoupling capacitor placement.
Intelligent Integration: Integrates MCU, sensors, and wireless modules (NFC/Bluetooth) to achieve device control, data acquisition, and wireless communication functions.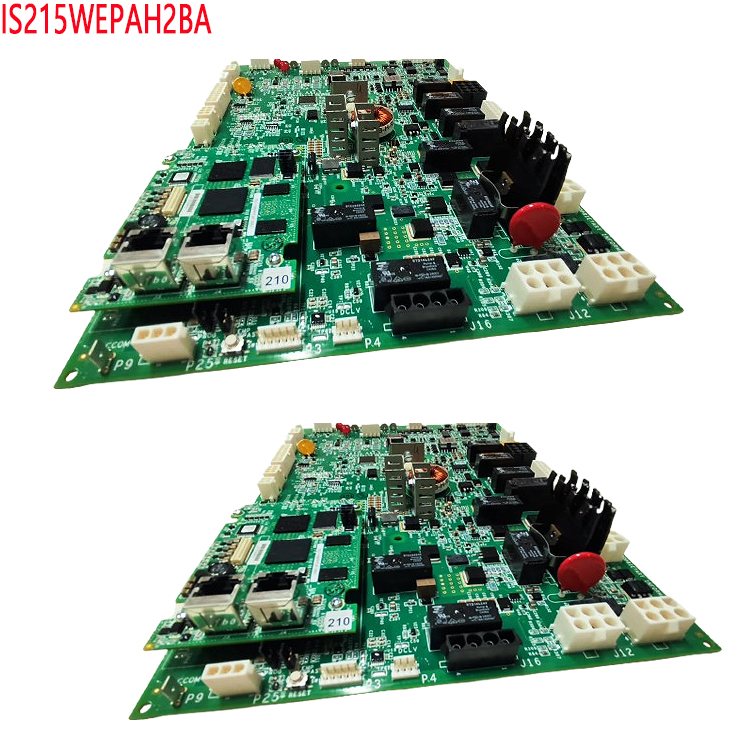
Reliability Assurance: Ensures stable operation in harsh environments through moisture-proof/shock-proof design, ESD protection, and thermal management (heat sinks/thermal conductive adhesive).
Precautions:
Maintenance: Regularly check the PCB solder joints, connectors, and component status to prevent poor contact or functional failure due to aging.
Design Specifications: Follow PCB design best practices, such as using a complete reference plane, controlling trace spacing, and avoiding slots on the reference plane to minimize the impact of parasitic parameters.
Environmental Adaptability: Marine/marine environments require moisture and salt spray protection; industrial environments require vibration and dust resistance; medical equipment must meet biocompatibility standards.
Electromagnetic Compatibility: High-frequency signals should be kept away from noise sources (crystal oscillators/switching power supplies), using shielding covers/grounding, and complying with CE/FCC certification requirements.
Signal Integrity: Avoid parallel signal traces, reduce the number of vias, control impedance matching, and use serpentine traces to compensate for delays.
Heat Dissipation and Safety: High-power components (such as power transistors) require heat sinks; avoid long, thin traces in power paths to prevent voltage drops; set test points at critical nodes for easy debugging.
Design and Manufacturing: Verify the consistency between the schematic and PCB layout, perform signal simulation (e.g., Altium Designer/PSpice), retain design documents and backups, and select a reliable PCB manufacturer to ensure impedance control accuracy (±10%).
Application Scenarios
Industry and Automation: Used in industrial control units (e.g., PLCs), robot control, sensor signal acquisition, and actuator driving to achieve precise control of production processes.
Core of Electronic Equipment: Used in computers, communication equipment (routers/base stations), medical equipment (ECG machines/ultrasound machines), automotive electronics (ECU/ABS), and aerospace navigation systems as a carrier for electrical connections and signal processing.
Data Storage and Transmission: PCB cards with integrated SD/MMC interfaces support high-speed data read and write, and are used in monitoring equipment, embedded systems, and financial terminals (ATMs/POS machines).
Special Applications: Marine power management (e.g., Mitsui AIO-B 2-0190), intelligent lighting, stage lighting control, weather monitoring stations, etc., adaptable to harsh environments such as humidity, vibration, and high temperatures.
Usage Methods:
Hardware Design:
Layout Rules: Digital/analog circuits should be partitioned; high-frequency signals should be short and thin; avoid corners below 90°; signal line length matching (e.g., the DAT0-DAT3+CMD group of an SD card requires a length tolerance of ±50 mils).
Power Management: Power line width ≥ ground line, radial layout; high current paths require low impedance design, with decoupling capacitors (0.1μF + 10μF) to suppress noise.
Interface Design: SD card slot selection (standard/Micro SD), SPI/SDIO mode selection, level matching (e.g., level converter required for 3.3V systems).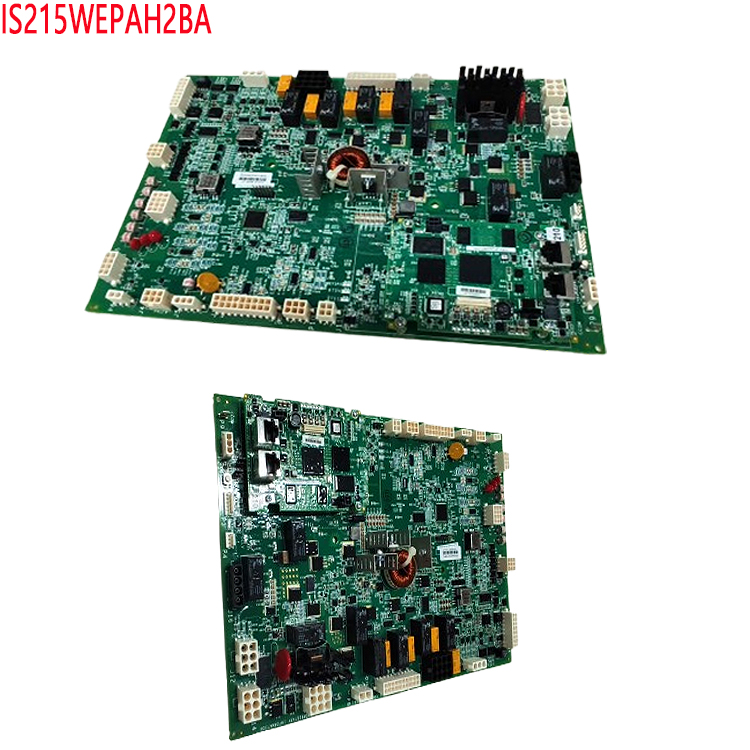
Software and Testing:
Driver Development: Implement SD card initialization, sector read/write, integrate FatFS file system; debug signal waveforms using a logic analyzer.
Soldering Process: SMD components use drag soldering/spot soldering, temperature control (320-350℃ for small components, 380-400℃ for chips), use anti-static tools, avoid cold solder joints/short circuits.
Functional Verification: Connectivity is tested with a multimeter, NFC/data transfer functions are tested with a dedicated APP/card reader, and full-function testing is performed after firmware flashing.
In summary, this PCB card, as the core carrier of electronic devices, has applications in multiple fields including industrial, consumer, medical, and aerospace. Its design needs to be optimized for specific scenarios (e.g., wiring, power supply, interfaces), and it must strictly adhere to manufacturing and testing standards to ensure performance and reliability.
All products on this website are special products, and market prices are constantly fluctuating.
Please refer to customer service for a quote, as the price is not accurate as it may be for new products.
Please confirm the model, product, price, and other detailed information with customer service before placing an order. This website is currently in use.
New products are available for sale; please contact customer service for further information.
Recommended related products:
MITSUI DIO-B PCB BOARD
MITSUI CPM-A PCB CARD
MITSUI CEP-C PCB CARD
MITSUI AIO-B 2-0190 PCB BOARD
MITSUBISHI MHI DIOUT-0201-RZA0237-96100066 PCB CARD
MITSUBISHI MHI DIOUT-0201-RZA0237-96100065 PCB CARD
MITSUBISHI MHI DIIN-0201-RZA0239-96100066 PCB CARD
MITSUBISHI MHI DIIN-0201-RZA0239-96100065 PCB CARD
MITSUBISHI MHI CPU-0202-RZA0227-96100070 PCB CARD
MITSUBISHI MHI CPU-0202-RZA0227-96100069 PCB CARD
More……



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.